List of contents
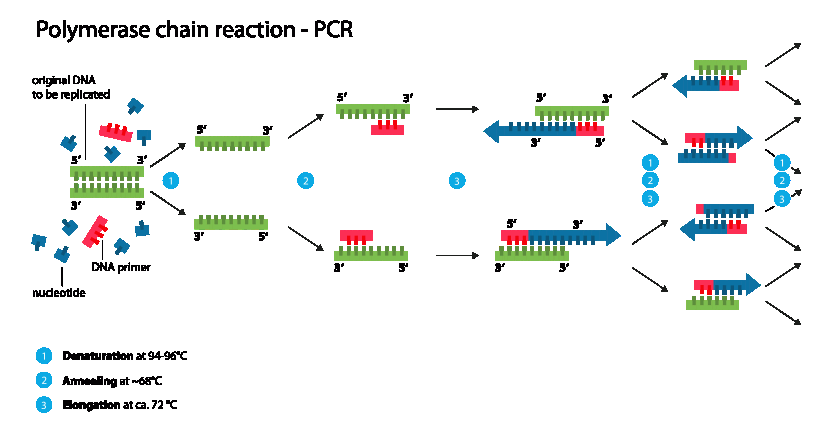
Polymerase Chain Reaction / PCR or known as polymerase chain reaction is a form of enzymatic DNA multiplication / replication technique without having to use organisms.
This PCR technique is widely applied in various types of fields, such as biochemistry, medicine and molecular biology.
Because this PCR technique is a technique that can be said to be quite practical and also cheap because it only requires a small sample to be able to produce DNA in large quantities and in a short time.
This makes this technique easier to apply than other propagation techniques.
There are 5 main components of PCR, below we will discuss one by one the main components of PCR.
Components in PCR
Various internal components Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) that is:
- DNA Template / mold, that is DNA double strand as a carrier for the base sequence of the fragment which will later be duplicated.
- DNA Polimerase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the polymerization of nucleotides into a DNA strand.
- Oligonucleotide primers, is a short single-stranded DNA / oligonucleotide that initiates and limits the DNA chain elongation / polymerization reaction.
- dNTP (deoxynucleoside triphosphate), is a metaphor for ‘bricks’, namely the building blocks of new DNA. There are four types of DNA dNTPs, namely dATP, dCTP, dGTP and also dTTP.
- Buffer, are chemicals that condition the reaction so that it can run more optimally and then stabilize it DNA polymerase.
- Ion Logam, acts as a cofactor DNA polymeraseand without this ion then DNA polymerase will not be able to work (generally Mg bivalent ions2+ and monovalent K+).
- Other reagents Apart from enzymes and primers, there are also other components that are involved in determining the success of the PCR reaction. These components are dNTPs for polymerization reactions and buffers containing MgCl2. Concentration of Mg ions2+ in reaction mixtures becomes very critical. Concentration of Mg ions2+ This will greatly influence the primary annealing and denaturation processes, product specificity, and enzyme activity and reaction fidelity.
Role and Function of PCR
PCR technique or Polymerase Chain Reaction has the following roles:
- As a simplification of the nucleotide sequence.
- As a determinant in determining the conditions of the nucleotide sequence that will experience mutations.
- Field of forensic medicine.
- To trace someone’s origins by comparing finger print.
Application of PCR Technique
The PCR technique is now widely used for various needs, including the following:
1. Gene Isolation
In isolating the insulin-producing gene from human genomic DNA and then inserting it into bacterial cells, a search DNA or better known as a probe with the same nucleotide base sequence as the desired gene is needed.
2. DNA Sequencing
is the sequence of bases in DNA that can be determined using techniques DNA Sequencingnamely the initial process is a PCR reaction or Polymerase Chain Reaction which uses one primer with the addition of
3. Forensics
It is an activity that when the process of physically identifying a victim is difficult to carry out.
So DNA testing is carried out by taking samples from any part of the victim’s body, then after that PCR analysis or Polymerase Chain Reaction to amplify certain parts of DNA which are usually called fingerprints.
Next, the results will be compared with DNA fingerprints belonging to families who are related by blood.
4. Disease Diagnosis
Polymerase Chain Reaction or PCR is one of the techniques that is often used to diagnose dangerous diseases such as Influenza A or (H1N1).
So that’s the information this time which discusses the components in PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction). Hope it is useful.
Also Read: Working Principles of PCR
All content and articles published on DomainJava.com are provided solely for informational and educational purposes. We strive to present accurate, relevant, and useful information, but it is not intended to violate any laws, policies, or guidelines. Any use of the information contained in the article Components in PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) is entirely the responsibility of the reader.