List of contents
Understanding Cell Respiration
The definition of cellular respiration is the process of breaking down food materials and later producing energy.
This respiration is carried out by almost all components of the body, whether animal cells, plant cells or human cells. This respiration is carried out at any time, whether during the day or at night.
As is known, the activities of living things require energy, including plants
This respiration occurs in all parts of the plant at a high level. Respiration occurs in the roots, leaves and stems chemically. Aerobic respiration in glucose is the opposite of photosynthesis. (Read: Understanding Photosynthesis)
For respiration, burning glucose by oxygen produces energy because all parts of the plant are made up of tissue and tissue is made up of cells, so respiration occurs in the cells.
Green plants actually breathe by taking oxygen from the environment, although not all plants breathe by using oxygen.
The purpose of breathing is actually to obtain energy and when this breathing event occurs, energy is also released.
Plants that often breathe anaerobically will get energy by breaking down certain materials so that they can still live.
In this breathing process, carbon dioxide and water vapor are released from the body.
Respiration in cells is a process where potential energy from nutrients is converted into energy that can be used by the plant or organism where the cell is located. This respiration occurs in both plant and animal cells.
Generally utilizes nutrients from glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, and energy. This cellular respiration usually involves oxidation to release energy but this respiration can be achieved without the presence of oxygen.
Types of cellular respiration
There are 2 basic types of cellular respiration, namely:
- Aerobics means using oxygen
- Anaerobic which does not use oxygen.
For aerobic respiration, it uses oxygen as a molecular breaker and releases adenosine triphosphate or what is often called ATP.
ATP is energy, this respiration does not require the presence of oxygen to produce ATP, fermentation itself is a form of anaerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration is also much faster than aerobic, but only produces 2 ATP per molecule.
In fact, according to one site, humans are capable of both aerobic and cellular respiration.
Also Read: Understanding Anaerobic Respiration
Differences in Respiration Between Aerobic and Anaerobic
Aerobic and anaerobic respiration are cellular respiration metabolic pathways shared by animals and plants.
These two biological processes will break down sugar that was previously synthesized during the photosynthesis process and become energy that can trigger cellular activity.
Even though they have the same purpose, aerobic and anaerobic respiration have completely different functions and operating pathways.
1. Presence of oxygen
Aerobic and anaerobic operate in very different oxygen environments, whereas aerobic respiration is carried out in the presence of oxygen, but anaerobic does not require oxygen at all.
2. Products of cellular respiration
Aerobic cellular respiration breaks down starch and sugar into carbon dioxide and water.
However, for anaerobic cellular respiration, it goes through a series of processes which are often called fermentation to break down sugar and starch into lactic acid or alcohol.
3. Alam
Aerobic respiration itself is a very common type of cellular metabolism found in many and all living organisms.
At the cellular level, almost all cells in plants and animals really need oxygen for efficient reduction. They reduce sugar and then convert it into energy molecules.
Anaerobic respiration is less common, because it is found in certain types originating from animal muscle cells and is a single cellular respiration method for various types of bacteria.
4. Energy production
The processes of aerobic and anaerobic metabolism are designed to release energy.
The type of energy that these cells produce is an energy molecule which is usually called adenosine triphosphate or what is often called ATP.
Aerobic cellular respiration is indeed much more efficient when creating ATP because from anaerobic respiration a glucose will produce approximately 38 ATP.
These glucose molecules will be the same and produce only 2 ATP through anaerobic respiration.
5. Inquality energi
Aerobic cellular respiration produces a lot of energy due to the presence of oxygen.
Because of the presence of oxygen, the molecules in starch and sugar will be able to pass through the cytoplasm and enter the mitochondria.
The sugar itself will be broken down so thoroughly that a lot of energy will be extracted through complex chemical processes.
Anaerobic respiration, on the other hand, cannot take up sugar molecules in the mitochondria, therefore it produces energy through the cytoplasm in a chemical process often called glycolysis.
Also Read: Understanding Aerobic Glycolysis
The equation of aerobic and anaerobic respiration
in humans, aerobic respiration requires oxygen which is used to provide energy for the body, anaerobic respiration does not require oxygen so it occurs in humans in a shorter period of time and during much heavier physical activities such as running or deadlifting.
1. Aerobic respiration
Many organisms undergo this respiration, for humans this respiration occurs all the time and provides energy for the body when carrying out various basic processes such as tissue repair, growth, and so on.
2. Anaerobic respiration
When an organism like yeast runs out of oxygen, it produces ethanol instead of water.
Like human muscles when they run out of oxygen. They will tend to produce lactic acid and not water.
Purpose of cellular respiration
The purpose of respiration in cells is to produce energy in a form that the organism can use.
Without respiration in cells, animals and even humans would not be able to survive because they would have no way to get the energy they need to maintain the organism.
Cell respiration process
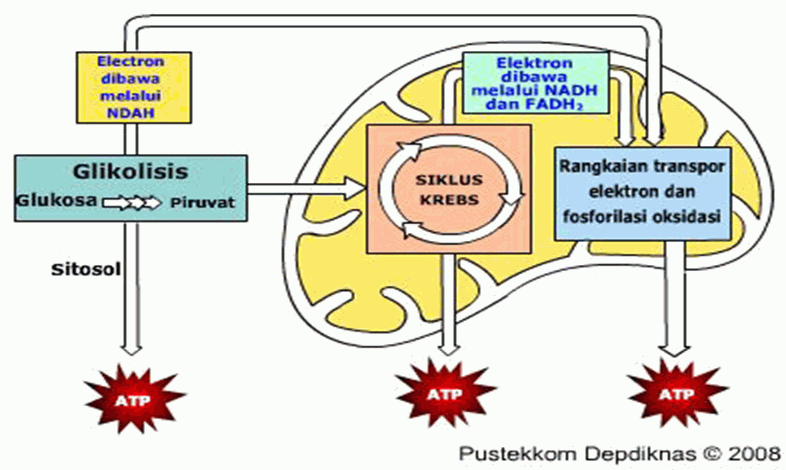
1. Glycolysis
Judging from the name, namely the words glico and lysis, it can be interpreted as the force used to break down sugar.
So why does it have to be sugar? You need to know that of the many food sources available, only sugar has the most energy-producing processes. Glucose itself can be obtained not only from sweet foods but also from types that contain carbohydrates.
In this first process, ATP or adenosine triphosphate will be converted into pyruvic acid which takes place in the cell organelle called cytoplasm.
2. Krebs cycle
After going through a stage called glycolysis, the results of this process, namely 2 ATP and 2 pyruvic acid, will directly enter the part of the cell called the mitochondria, the processing absolutely requires oxygen as a catalyst.
If the first stage produces pyruvic acid, then the pyruvic acid will be converted into ATP.
The chemical reaction that occurs changes pyruvic acid into the acetyl CoA compound, then continues with a series of chemical reactions to produce 2 ATP. In total there are 4 ATP obtained from the Krebs cycle and also glycolysis.
3. Electron transport
This is the final part and produces the most ATP, there is no series of chemical reactions as above, only several equations are used to assemble ATP in larger quantities.
This process takes place in organelles, namely cell mitochondria. This system really needs several compounds that are no longer used in previous reactions, such as NADH and FADH.
In the end, the results are quite large, namely that it can provide 32 to 34 ATP which will later be used as human energy.
A byproduct of cellular respiration
During this respiration process certain by-products are released along with ATP. In aerobic respiration, water and carbon dioxide are the main wastes in respiration.
Important Things About Cell Respiration
All kinds of processes that occur in the body definitely require energy. Even though a person has a lot of food intake, it provides various kinds of important ingredients that are needed.
This process of cell metabolism converts materials into a form that can be used for the body’s needs.
Cellular respiration also involves how cells can convert food into energy for cells, the body and tissues.
1. Cellular respiration
This process of cellular respiration occurs in the cell cytoplasm and mitochondrial organelles.
After the digestive system breaks down food materials into carbohydrates, lipid and protein molecules, cells can also convert these materials into energy, glucose molecules and types of sugar are the main source of energy and appear at the beginning of the process of cellular respiration.
A series of chemical pathways work to convert molecules from glucose to adenosine triphosphate or what is often called ATP. The actual fuel for the cells.
2. Glucose
Glucolysis marks the first stage in cellular respiration, glucose molecules are broken down into a material often called pyruvate.
The results of this series of stages produce 2 molecules of ATP which are often used throughout the respiration process.
These two conditions, namely aerobic and anaerobic, occur in a series of stages of respiration. However, glycolysis can continue whether oxygen is present or not.
One example of this anaerobic glycolysis process can be seen when the muscles have exhausted their oxygen supply.
This glycolysis also continues even though there is a buildup of pyruvate in the cells which can cause muscles to burn and become sore.
3. Oxygen
The Krebs cycle is stage number 2 of the cellular respiration process, and is made possible by the presence of oxygen in the cells.
When these oxygen molecules are available, the pyruvate produced during the glycolysis stage can be transported from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria, where the Krebs cycle takes place.
At this stage it consists of various kinds up to a series of k paths an chemical that can produce 2 additional ATP molecules as well as carbon dioxide.
This carbon dioxide molecule is a byproduct of the process and is transported out of the cells by the respiratory system.
Until the end of this respiration cycle, the 36 available molecules are used by the cell.
4. ATP
ATP is generally known as one of the fuels and energy sources of cells because it is the most important function it can play.
Without this material, cells and body systems would not be able to defend themselves on their own, apart from their role as fuel.
This is also recycled. After these cells use ATP molecules are produced through cellular respiration. ADP and phosphate molecules are residual byproducts.
Phosphate and ADP are raw materials needed to produce ATP.
5. Life cycle
The life cycle is an indispensable process for most living organisms, although different organisms can carry out this process in different ways.
Plant organisms also carry out and produce energy from cell processes using the sun.
One of the by-products is oxygen, this is important for the exchange of carbon dioxide from animals and oxygen.
That is our discussion on this occasion regarding the meaning of cellular respiration: types, goals, processes and products. Hope it is useful.
All content and articles published on DomainJava.com are provided solely for informational and educational purposes. We strive to present accurate, relevant, and useful information, but it is not intended to violate any laws, policies, or guidelines. Any use of the information contained in the article The definition of cellular respiration is: type, purpose, process and product is entirely the responsibility of the reader.