Connectivity of DNA with RNA – Every living cell on this earth is always equipped with a role of nucleic acid which comes from the composition of DNA and RNA.
DNA itself actually has a certain genetic code that is able to regulate a function in cells through the formation of proteins.
When the DNA in the nucleus is transcribed into a form of RNA, this process will then be able to penetrate the pores of the nucleus to enter the cytoplasm.
It should be noted that the transcription process is a transfer of genetic information contained in cells between DNA and RNA.
As occurs in the process of forming proteins in the body, where genes which are part of DNA instruct cells to create a certain protein.
After receiving this order, RNA and DNA begin to collaborate to produce this existing protein using the cell’s genetic code.
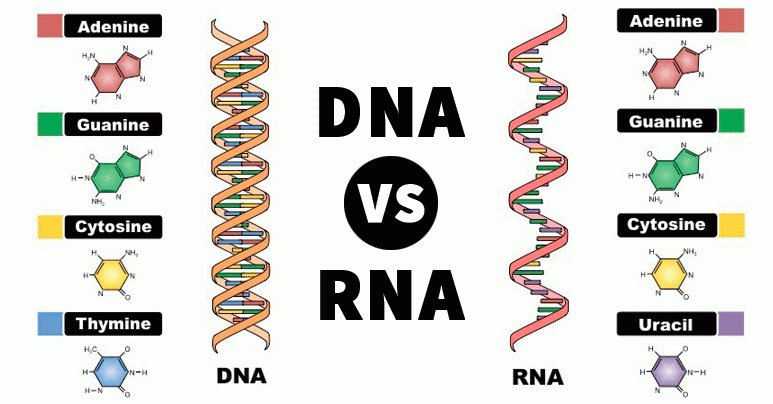
In fact, if we look more closely, the arrangement or composition of RNA is slightly different from the arrangement of DNA.
Here are a few differences that you might need to know in terms of arrangement, as follows:
- If DNA has deoxyribose sugar, RNA has quite high levels of ribose sugar,
- RNA does not have the nitrogen base Thymine where this nitrogen position is replaced by uracil which usually has a single strand.
When the transcription process occurs, an enzyme called RNA polymerase uses the genes in DNA as a place to assemble RNA strands or what is usually called mRNA.
In principle, RNA polymerase functions as an unbuttoner for the part of DNA that is to be copied in two single grooves.
Next, this polymerase will read the basic molecules in DNA and then create an mRNA strand using the existing complementary base molecules.
This translation occurs in the cell’s ribosomes where ribosomal RNA or rRNA also resides. Then cells begin to use mRNA and also transfer RNA (tRNA) to create amino acids, where these amino acids are used to form a protein.
It should be noted that there are 20 essential amino acids, each of which is represented by a three-base bond in mRNA which is usually referred to as a codon.
These specific tRNA strands will then correspond to each part of the codon. Next, the tRNA part or segment will transport the amino acids that have been successfully produced.
In a ribosome, which contains tRNA and protein elements, its location is usually always attached to an mRNA strand.
Meanwhile, segments of tRNA that correspond to each codon on the mRNA are also attached to the strand.
Bonds found in tRNA and mRNA, as is the case with amino acids carried by tRNA.
These amino acids will then bind to each other and immediately proceed to form a new amino acid chain.
So it can be said that in carrying out its function as a regulator of every cell activity, DNA transcribes itself into the form of RNA, where this RNA then has a large and direct role in the formation of proteins.
The RNA that is already in the ribosome then also goes through a translation process where it will be translated as a codon on the mRNA by tRNA.
This process will then create an arrangement of amino acids that form proteins, which have functions as functional, structural and regulatory proteins.
That’s our discussion on this occasion regarding the connectivity of DNA and RNA. Hope it is useful.
Also Read: Difference between DNA and RNA
All content and articles published on DomainJava.com are provided solely for informational and educational purposes. We strive to present accurate, relevant, and useful information, but it is not intended to violate any laws, policies, or guidelines. Any use of the information contained in the article Connectivity of DNA with RNA is entirely the responsibility of the reader.