List of contents
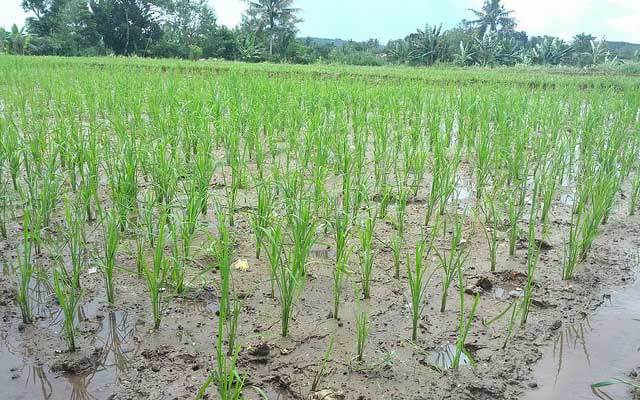
The method of cultivating rice plants using the SRI method is expected to provide additional rice production of 1 – 2 tons per hectare of rice fields.
SRI was first developed by French priest And Fr. Henri de Laulanie, S. J IN Madagascar in early 1980. SRI then became known in several countries in the world, including Indonesia, in 1997.
In its implementation, there are several basic principles that become provisions in the rice cultivation technique using the SRI method, namely as follows:
Principles of SRI Method Rice Cultivation
- Seedlings are planted at a very young age, namely seeds that are less than 12 days after sowing (hss) – when the seedlings still have two leaves.
- Then the seeds are planted in a pattern of one hole for one plant, with a spacing of 25 x 25 cm or 30 x 30 cm or more rarely, you can also use the legowo 2 row system.
- Seedlings are planted at a young age and are still weak. Transplanting must be done as soon as possible (less than 30 minutes) and extra care must be taken so that the roots are not broken and planted shallowly
- The soil is not irrigated continuously, a maximum of 2 cm of water is given (various) and a certain period is dried until it breaks (intermittent/interrupted irrigation)
- Optimize land cultivation by plowing to increase soil aeration
- Weeding from the start at around 10 days of age and repeated 2 – 3 times with 10 day intervals, wherever possible using organic fertilizer and organic pesticides to maintain soil quality and maintain the balance of soil biota. Also Read: Understanding Organic Fertilizer
How to Cultivate Rice Plants using the SRI Method
1. Land Management
The land is processed like planting rice using the usual method, namely the land is plowed to a depth of 25 to 30 cm while burying the remains of weeds and grass, then loosened using a rake, then leveled as best as possible so that when water is added, the height in the rice fields will be even.
2. Ditch
On SRI plots, ditches should be made around and across the plot to remove excess water. The location and number of drainage ditches are adapted to the shape and size of the plot, as well as the dimensions of the irrigation channel.
3. Selection of Good Seeds
To get good quality seeds, the seeds are first tested by selecting them using a salt water solution. The seeds that sink are good quality seeds, then wash them with plain water until they are clean.
4. Soaking Seeds
The seeds that have been tested are then soaked in plain water, with the aim of softening the grain husks so that they can speed up the seeds to germinate. Soaking is done for 24 to 48 hours.
5. Aerating the Seeds
The seeds that have been soaked are then removed and put into a porous sack, with the aim of allowing air to enter the rice seeds, then stored in a damp place. Airing is carried out for 24 hours.
6. Seed Nursery
Seed sowing is done using a winnowing pan or basket or also in rice fields. The seeds, which have been aired, are sown into a basket filled with soil.
After the seeds are sown, cover them with a thin layer of soil. During the spring season, water is given every day to keep the media moist and the plants stay fresh.
7. Plastering
Before planting, weeding is done first using ticks so that the spacing of the rice fields is straight and neat so that it is easy to weed.
8. Planting
Planting rice seeds must be shallow with a depth of 1 – 1.5 cm, and the measurement when planting is like the letter L so that the rice field is not flooded when planting.
9. Fertilization
Fertilization is carried out up to three times in one growing season. Because the SRI method of rice cultivation is organic cultivation, the fertilizer used must be organic, namely manure or compost that is completely mature.
Fertilization is carried out three times, fertilization 1 is carried out at the age of 7 – 14 days of age, fertilization 2 at the age of 20 – 30 days of age, and fertilization 3 at the age of 40 – 45 days of age.
Read Also:
- Dosage and Benefits of Urea Fertilizer for Rice Plants
- Easy Way to Make Husk Charcoal from Rice
10. Pest and Disease Management
It should be remembered that the SRI method is an organic-based plant cultivation, so as much as possible avoid the use of chemical pesticides to control rice plant pests.
11. Harvest
The harvesting process can be carried out after the plant is declared old, marked by full and even yellowing of the grain.
Harvest with the SRI method is usually earlier than with the regular method, calculated from the day the seeding starts.
Advantages of the SRI Method
- Save water: the SRI method of rice cultivation irrigation techniques uses an intermittent irrigation system or an intermittent irrigation system. Therefore, there is a period of irrigation and a period of drying. Irrigation is only done at a height of 5 mm – 2 cm, thereby saving water use.
- Save seeds: using this method, one seed is planted in one hole, so that for 1 hectare of land you only need 5 kilograms of seeds. This of course saves the use of seeds.
- Saves time: this method requires planting seeds at a young age, namely under 12 days after sowing (hss) so that harvest time can be faster. Thus, maintenance costs can be reduced.
- Increased production: rice production can increase from 50 to 100% compared to general methods. In some places, production can reach 11 tons per hectare of rice fields.
- Environmentally friendly: gradually, the use of chemical fertilizers (Urea, SP36, KCl) will be reduced and replaced with organic fertilizers (compost and manure), as well as the use of organic pesticides.
Weaknesses of the SRI Method
- With this system, farmers will be wasteful in using compost.
- There are times when it is difficult to get manure so it will disrupt the cultivation process.
- If you have a large area of land, you will need quite a lot of labor for planting.
- There are technical obstacles to the implementation of SRI components that could occur during rice seed planting activities.
- If the planting is done shallowly and one plant is planted, the risk is quite large, especially when it rains, what must be done is replanting and additional labor costs.
- Easily attacked by OPT.
Benefits of the SRI Planting Method
In general, the process and method of cultivating rice plants using the SRI method has several benefits, including:
- Can save water. The water requirement in this cultivation system is around 20 to 30% compared to conventional methods.
- It can restore soil fertility and health so that it can create balance in the ecology in the soil.
- Forming ideas and creativity from farmers so they can research and become professors on their own land. Of course, this doesn’t depend on chemicals such as chemical fertilizers and chemical pesticides, the prices of which are getting more expensive every day.
- Help open up employment opportunities in rural areas so that it can reduce unemployment and increase family income.
- Able to produce high rice production and is free from chemical residues.
- Passing on healthy soil to the next generation.
That is the explanation and review of how to cultivate rice plants using the SRI method.
Hopefully the agricultural products you are working on will gain abundant profits. Hope it is useful.
All content and articles published on DomainJava.com are provided solely for informational and educational purposes. We strive to present accurate, relevant, and useful information, but it is not intended to violate any laws, policies, or guidelines. Any use of the information contained in the article How to Cultivate Rice Plants using the SRI Method is entirely the responsibility of the reader.